And Linux Command; && in Linux, logical operators are used in various contexts, including shell scripting and command line operations. Logical operators are used to perform logical operations on values or conditions, and they are typically used within conditional statements to control the flow of a script or to evaluate expressions.
What is the And Linux Command?
The "And Linux Command" (&&) can be used to chain commands, running them inline sequentially one after the other. This can be extremely useful in situations where it's important to ensure that each command completes successfully before moving on to the next line of code.
The symbol && which makes up the And Linux Command is commonly referred to as the "AND operator" or the "logical AND operator".
You can use && in bash shell scripts or command line operations as shown below:
How to chain commands using && operator
The syntax for using the logical AND operator is to separate each command with the two ampersands (&&). To use it to chain multiple commands, simply type the first command, followed by &&, second command &&, third and so on. Multiple commands can be daisy-chained into a string.
For example, here are three chained commands on one single line or string of code:
command1 && command2 && command3How the And Linux && command chain works:
In the example shown above, we are using "And Linux Command" && to run multiple commands sequentially (one after the other). In this case, command1 is executed first. If command1 completes successfully, then command2 will be executed next. If command2 is also successful, then command3 will finally be executed. However, if any of the chained commands fail or return an error, subsequent commands after it will not be executed.
Tip * The next command only runs if the previous command exits with a success status (i.e., exit status 0).
Additional Use Cases of the And Linux Command (&&)
The logical AND operator (&&) can be extremely useful in various scenarios. Below are some additional real-world examples.
1. Updating and Cleaning Up a Linux System
To update the package list, upgrade all installed packages, and remove unnecessary ones, use:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y && sudo apt autoremove -yExplanation:
sudo apt update– Updates the package list.sudo apt upgrade -y– Upgrades all installed packages.sudo apt autoremove -y– Removes unnecessary dependencies.
If any command fails, the following commands will not execute.
2. Compiling and Running a C Program
For developers compiling a C program, you can use:
gcc program.c -o program && ./programThis first compiles program.c, and if there are no errors, it runs the compiled program.
3. Creating a Directory and Moving Files
If you need to create a directory and move files into it:
mkdir backup && mv *.txt backup/This ensures that the directory is created before moving all .txt files into it.
How to Copy a File and Then Delete the Original
To copy a file named "file.txt" to a directory named "backup" and then delete the original file, you would use the "cp command" like this:
cp file.txt backup/ && rm file.txt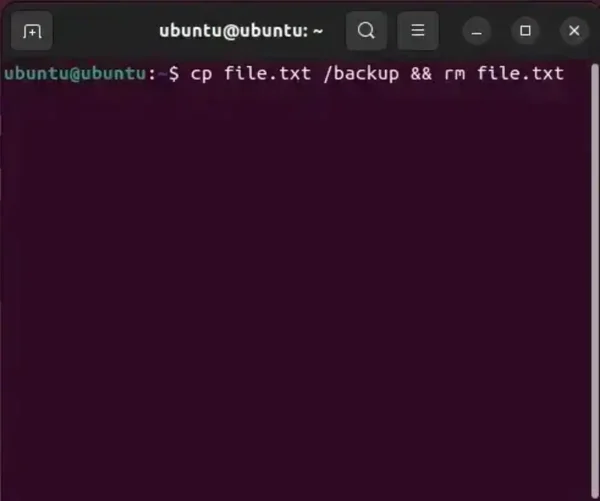
This code will copy the file to the backup directory (assuming it exists), and if the copy was successful, it will proceed to remove the original file. If copying fails, the second chained "rm command" to remove the file will not execute.
Move an Entire Directory and Then Delete the Original
To recursively copy an entire directory, including any subdirectories and files within, to a "backup" directory, and then delete the original directory, you could chain the "cp and rm commands" as follows:
cp -r folder/ backup/ && rm -rf folderThis command copies the entire "folder" along with any subfolders and files within, recursively using option (-r) to our "backup" directory (preserving the folder contents). Then, only if copying was successful, the original folder will be recursively (-r) and forcefully (-f) deleted.
Understanding Other Logical Operators in Linux
Besides &&, Linux provides other logical operators for scripting and command chaining.
Using the OR Operator (||)
The OR operator || executes the second command only if the first one fails.
mkdir my_folder || echo "Failed to create directory"If mkdir my_folder succeeds, the echo command won't run.
Combining AND and OR Operators
You can combine && and || to create complex conditions:
[ -f "data.txt" ] && echo "File exists" || echo "File does not exist"Logical Operators in Shell Script
Logical operators are often used in combination with if statements or within scripts to control the behavior of the script based on the success or failure of certain commands.
Here's an example of how logical operators can be used in a shell script:
#!/bin/bash
file="example.txt"
# Check if the file exists and is readable
if [ -f "$file" ] && [ -r "$file" ]; then
echo "File exists and is readable."
else
echo "File does not exist or is not readable."
fiIn this example, the && operator is used to combine two conditions: one checks if the file exists (-f "$file") and the other checks if the file is readable (-r "$file"). The if statement evaluates the combined condition and executes the appropriate branch of code based on the result.
Final Thoughts on Using the && Command in Linux
To conclude, those were just a few examples of how to run multiple commands in sequential precession by using the logical AND operator (&&). Hopefully, this section has helped you better understand how to chain commands on Linux or Unix-based systems.
If you found this article useful, you might also be interested in learning how to:
