Recover Lost Space on a USB flash drive: Missing space on your USB drive after formatting or creating a bootable USB? Is your USB drive showing the wrong capacity? You may have encountered this issue after using tools to burn an ISO to a USB. Don't worry, recovering lost space on a USB flash drive in Windows, Linux, or even macOS is pretty straightforward.

Recovering Lost Space on a USB Flash Drive
This comprehensive guide explains why USB storage capacity may go missing and provides simple instructions to fix the issue on both Windows, Linux, and macOS systems. Whether your USB drive is showing the wrong capacity, appears to be a corrupted flash drive, or has missing storage, these easy-to-follow steps will help you restore it to its full capacity and functionality. Read on to understand what causes this problem and learn how to recover lost space on a USB drive quickly and effectively.
Why Does USB Drive Storage Space Go Missing?
When you burn an ISO to a USB drive using tools like Balena Etcher, the drive's filesystem is reconfigured to match the ISO file. This process often leaves the remaining storage space unallocated, rendering it unusable for traditional storage purposes. In some cases, your USB may even appear as a corrupted flash drive with reduced capacity.
For example, tools like dd (Disk Dump) overwrite the USB's original partition table, limiting its usable size to the ISO file's size. This is particularly problematic for USB drives with significantly larger capacities. To fix this, you need to reallocate the unallocated space by creating a new partition.
Recover Lost Space on a USB Drive (Windows)
To recover lost space on a USB flash drive, use Windows Disk Management to create a new volume from the unallocated space. Assign a drive letter to the new volume, then format it with a file system of your choice. Here's how:
- Access the Windows run box by pressing the Win+R keys. Then type
diskmgmt.mscand press Enter to open Disk Management.diskmgmt.msc - Next, to create a New Volume from the remaining space on your USB drive:
- Locate your USB Disk from the list.
- Right-click the Unallocated Space and select New Simple Volume.
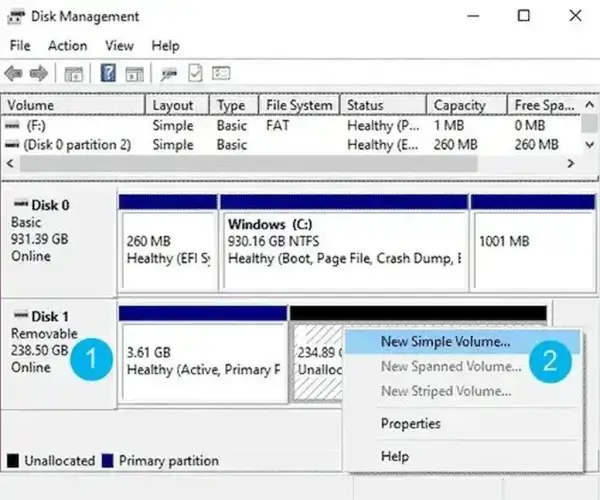
- When prompted, click Next to start the "New Simple Volume Wizard".
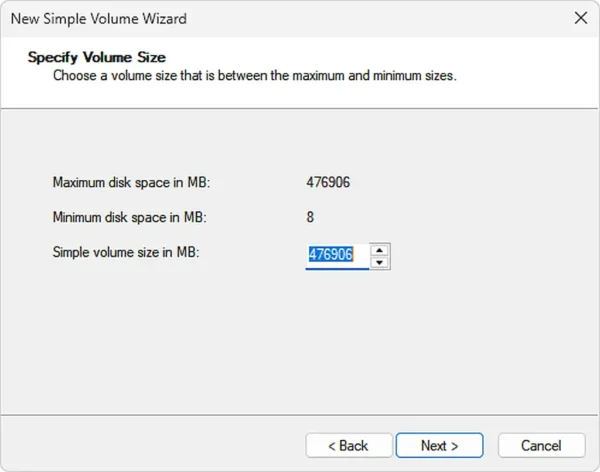
- Specify a Simple Volume size or leave it as is to use the remaining disk space. Click Next to use all of the remaining space.
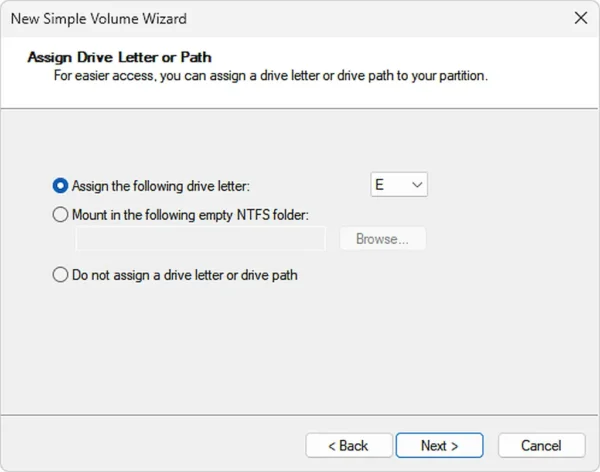
- Assign a drive letter or leave it as is. Click Next.
- Finally, create a new volume using only the unallocated space:
- Select a File system.
- Create a Volume label.
- Click Next.
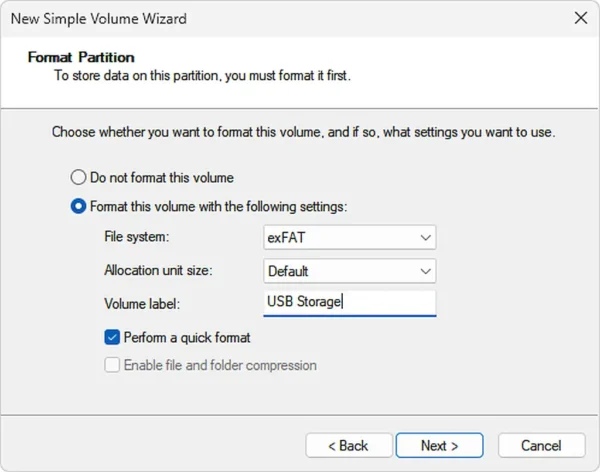
- Click Finish to complete the creation of the new partition.
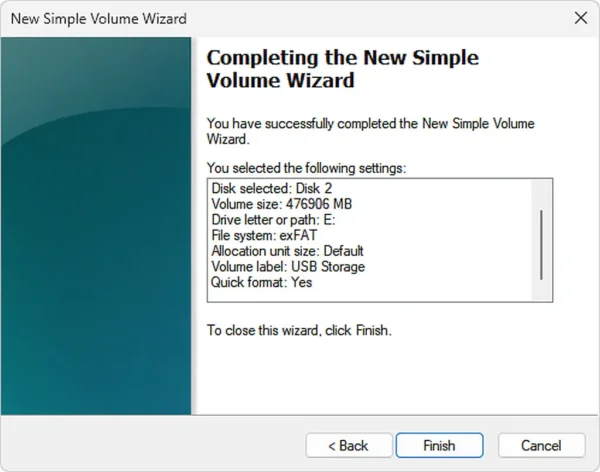
If all went well, you should now have access to the once missing space on your USB drive via the newly created volume and related assigned drive letter.
Recover USB Drive Space in Linux Using Parted
The following creates a new partition using mkpart only in unallocated space and does not affect existing partitions.
- Open a terminal window (Ctrl+Alt+T in Ubuntu/Debian).
- Run
partedwith superuser privileges and specify your USB drive:sudo parted /dev/sdX
(Replace /dev/sdX with your actual USB device letter.)
- List existing partitions and find unallocated space:
print
- Create a new partition in the unallocated space using the
mkpartcommand:mkpart primary ext4 START END
Explanation:
START= the starting point of the unallocated space (e.g., 1MiB or the next free sector after the last partition).END= the endpoint of the partition (usually the maximum available space, e.g., 100% of remaining free space).
You can see exact values from the
printcommand output. For example, if your unallocated space starts at 1MiB and ends at 15.5GiB, you would type:mkpart primary ext4 1MiB 15.5GiB
- Exit
partedby typingquit.
After creating the partition, format it with your desired filesystem (e.g., mkfs.ext4 /dev/sdX1).
Tip: Always double-check the device name using lsblk or fdisk -l to avoid accidentally formatting the wrong drive.
Recover Lost Space on a USB Drive (macOS)
macOS can reclaim missing USB storage by expanding an existing partition or claiming unallocated space without erasing current data. This commonly occurs after writing an ISO to a USB drive using tools such as Etcher or dd.
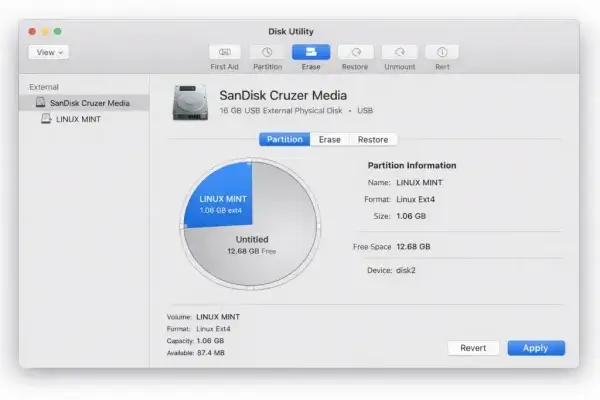
Method 1: Use Disk Utility (GUI)
- Insert the USB flash drive.
- Open Disk Utility
Applications → Utilities → Disk Utility - In the menu bar, click View → Show All Devices.
- Select the USB device itself (not the volume listed beneath it).
- Click Partition.
If Disk Utility detects unallocated space, it will appear as a gray segment in the partition map.
- Select the existing partition.
- Drag the resize handle to expand the partition into the unallocated space.
- Click Apply to confirm.
macOS will extend the existing filesystem to use the missing space without erasing the drive.
Note: If the resize option is unavailable, the ISO may have created a fixed partition layout that Disk Utility cannot expand. In that case, use the Terminal method below.
Method 2: Recover Unallocated Space Using Terminal (diskutil)
This method preserves the existing partition and only claims unused space.
- Open Terminal.
- List all disks:
diskutil list - Identify your USB device, for example
/dev/disk2. - Check the partition layout:
diskutil info /dev/disk2 - Expand the main partition to fill all available space:
sudo diskutil resizeVolume /dev/disk2s1 100%
Replace disk2s1 with the correct partition identifier for your USB drive.
If successful, the existing volume will grow to include all unallocated space without reformatting.
Tip: If the bootable USB was completely overwritten with dd using a Linux ISO, the partition type may appear as Linux or ISO9660. In these cases, macOS might still require recreating the partition map, which does erase data. Back up any important files first if needed.
Troubleshooting USB Lost Storage Space
- Eject and reconnect the USB drive: Sometimes a simple reconnection resolves detection issues.
- Check Device Manager (Windows): Open Device Manager and look for any warning icons or driver issues under the USB or disk drives section. If necessary, update or reinstall the device drivers.
- Use
lsblkorfdisk -l(Linux): These commands list all connected drives and partitions. Verify that your USB drive is recognized correctly and identify its device name. - Restart your computer: Rebooting can help resolve system-level issues with USB detection.
- Test the USB drive on another computer: If the issue persists, it may indicate a problem with the USB drive itself.
- Run a diagnostic tool: Use tools like
chkdsk(Windows) orfsck(Linux) to check for and repair errors on the USB drive. - Check for Fake USB Drives: Some USB drives, especially those purchased at a discount or from unverified sources, may have falsified storage capacities. Use tools like H2testw to verify the actual capacity.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Why does my USB drive show less space than it should after formatting?
This usually happens when an ISO is burned onto the USB drive, and the remaining storage becomes unallocated or unusable. The partition table may be overwritten, limiting the drive's capacity. Reallocating the unallocated space can fix the issue.
Can I recover lost space on my USB drive in both Windows and Linux?
Yes, you can recover lost space on your USB drive using Disk Management on Windows or the parted command-line tool on Linux. Both systems offer methods to create a new partition and restore the missing space.
What should I do if my USB drive is still not showing the full capacity?
Try troubleshooting by ejecting and reconnecting the USB, checking the device manager (on Windows), running disk-checking tools like CHKDSK or fsck, and ensuring the drive is genuine. If the problem persists, it could indicate hardware failure.
How do I verify if my USB drive is a fake?
If your USB drive shows incorrect storage capacity or behaves unpredictably, use tools like H2testw to test for fake drives. This tool will help confirm the actual capacity of the drive.
Final Take on How to Restore Capacity of a USB
Whether you're running from Windows, Linux, or macOS, recovering lost space on a USB flash drive is a simple restoration process that can easily be done by anyone with access to the right tools. If your pen drive appears to be corrupted or just showing the wrong capacity after burning an ISO, you can use the methods outlined in this guide to recover lost space and restore your bootable USB stick to its full capacity once again.
