Learn How to Set Up Ubuntu Remote Desktop Access for Remote Control and Screen Sharing: This updated guide shows you how to set up Ubuntu Remote Desktop Sharing using the built in GNOME Remote Desktop with either VNC or RDP support.
Whether you're working from home, managing a remote workstation, or providing technical support, Ubuntu remote access offers flexibility, convenience, and cross platform compatibility.
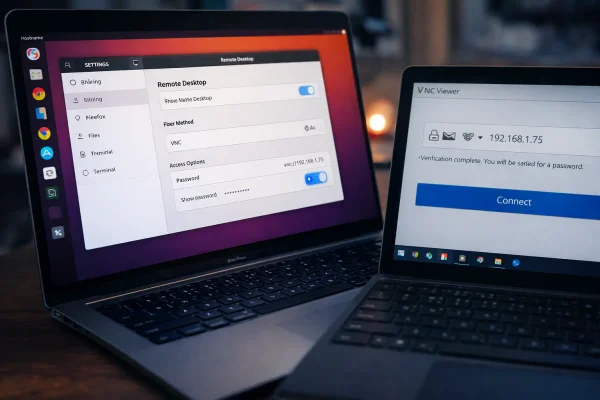
Ubuntu Remote Desktop Access: Overview
Modern Ubuntu versions include GNOME Remote Desktop, which replaces older tools such as Vino. It allows you to securely share your desktop using either VNC or RDP without installing third party servers.
This guide applies to Ubuntu 20.04 and newer, with Ubuntu 22.04+ as the primary focus.
Benefits of Ubuntu Remote Desktop Screen Sharing
Ubuntu Remote Desktop allows you to control your system without being physically present. Key advantages include:
- Remote administration: Access your system from another room or location.
- Cross platform support: Connect from Windows, Linux, or macOS.
- Built in solution: Maintained by GNOME and included with Ubuntu.
Important: GNOME Remote Desktop requires an active logged in user session.
Note: GNOME Remote Desktop does not start a virtual desktop session; a user must be logged in locally.
Prerequisites
- Ubuntu 20.04 or newer
- GNOME desktop environment
- A second device running Windows, Linux, or macOS
- A VNC or RDP client such as RealVNC Viewer or Remmina
Enable Ubuntu Remote Desktop Access
Here are the simple steps to enable the built in remote desktop access in Ubuntu:
Enable Remote Desktop in Ubuntu Settings
- Open Settings.
- Navigate to Sharing.
- Toggle Sharing to On.
- Click Remote Desktop.
From the Remote Desktop panel:
- Enable Remote Desktop.
- Select VNC or RDP.
- Set a strong access password.
- Make a note of the displayed hostname or IP address.
Understanding VNC vs RDP
VNC and RDP are both protocols for remote access, but they work differently:
- RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol): Creates a separate virtual session. It is highly efficient, fast, and includes built-in security with SSL/TLS. Best suited for performance-focused connections, especially when connecting from Windows clients.
- VNC (Virtual Network Computing): Shares the actual physical screen of the Ubuntu system. It sends pixel data over the network, making it more versatile and compatible across platforms, including Windows, Linux, and macOS. Ideal for collaboration or cross-platform support, but slightly slower than RDP. Security typically requires SSH tunneling or a VPN.
Summary: Use RDP for speed and efficiency, especially for Windows to Ubuntu connections, and use VNC when you need cross platform compatibility or want to interact with the actual desktop session.
VNC vs RDP Comparison
| Feature | VNC | RDP |
|---|---|---|
| Best for | Cross platform access | Windows clients |
| Performance | Moderate | Better on Windows |
| Encryption | Basic | Stronger by default |
| Wayland support | Limited | Better |
| Ease of setup | Very easy | Very easy |
Wayland vs Xorg Notes
Ubuntu uses Wayland by default. GNOME Remote Desktop works under Wayland, but some VNC clients have limited feature support. If you encounter issues such as a black screen:
- Log out of your session.
- Click the gear icon on the login screen.
- Select Ubuntu on Xorg.
- Log back in and retry the connection.
Find Your Local IP Address
- Open Settings.
- Click Network.
- Select the gear icon next to your connection.
Alternatively, use the terminal:
ip aUbuntu Remote Desktop Access from Windows
These instructions show how to connect from a Windows computer to your Ubuntu desktop using either VNC or RDP. Follow the steps below depending on the method you prefer.
Using VNC Viewer for Ubuntu Remote Desktop (Windows)
- Download and install VNC Viewer.
- Enter your Ubuntu system's IP address.
- Authenticate using the Remote Desktop password.
Using RDP for Ubuntu Remote Desktop (Windows)
- Open Remote Desktop Connection.
- Enter the Ubuntu IP address.
- Log in with your Ubuntu username and password.
Ubuntu Remote Desktop Access from Linux
Linux users can use Remmina or other VNC/RDP clients to connect to Ubuntu desktops. Choose the protocol that fits your workflow.
- Install Remmina:
sudo apt install remmina - Launch Remmina.
- Select VNC or RDP.
- Enter your Ubuntu IP address and authenticate.
Ubuntu Remote Desktop Access from macOS
macOS provides built in VNC support through Screen Sharing and RDP via Microsoft Remote Desktop. Use the instructions below depending on which method you want to use.
Using VNC (Screen Sharing) for Ubuntu Remote Desktop (macOS)
- Open Finder and press Command + K or go to Go → Connect to Server.
- Enter your Ubuntu IP with
vnc://(e.g.,vnc://192.168.x.x). - Click Connect and enter your Remote Desktop password.
Using RDP (Microsoft Remote Desktop) for Ubuntu Remote Desktop (macOS)
- Download Microsoft Remote Desktop from the Mac App Store.
- Open the app and click Add PC.
- Enter your Ubuntu IP and login credentials.
- Double click the PC entry to connect.
Security Considerations
- Avoid exposing VNC/RDP ports directly to the internet.
- Use an SSH tunnel or VPN for remote access.
- Consider NoMachine for encrypted remote connections.
Troubleshooting
- Connection refused: Ensure Remote Desktop is enabled and the user is logged in locally.
- Black screen: Switch from Wayland to Xorg.
- Authentication failed: Check Remote Desktop password and username.
Alternatives to GNOME Remote Desktop for Ubuntu
- NoMachine - High-performance remote access
- Chrome Remote Desktop - Browser-based access
- XRDP - Windows style remote desktop
- SSH with X11 forwarding - Command-driven workflows
Frequently Asked Questions
Which Ubuntu versions support GNOME Remote Desktop?
Ubuntu 20.04 and newer include GNOME Remote Desktop, with Ubuntu 22.04+ having full built-in VNC and RDP support.
Do I need to install VNC or RDP servers manually?
No, GNOME Remote Desktop includes both VNC and RDP support out of the box.
Can I connect from macOS?
Yes. You can use the built-in Screen Sharing app (VNC) or Microsoft Remote Desktop (RDP) to connect.
Is it safe to expose my Ubuntu desktop to the internet?
Direct exposure is not recommended. Use a VPN, SSH tunnel, or encrypted remote tools like NoMachine.
Can I use GNOME Remote Desktop on a headless system?
GNOME Remote Desktop requires a logged-in session. For fully headless systems, alternatives like NoMachine, XRDP, or SSH are recommended.
Final Notes on Ubuntu Remote Control
Modern Ubuntu Remote Desktop Access and screen sharing using GNOME Remote Desktop provides a secure, cross platform, built in solution. Following this guide ensures reliable Ubuntu remote control whether you are on Windows, Linux, or macOS.
