Updating Linux: Keeping your Linux system updated is essential for maintaining stability, improving performance, applying security patches, and gaining access to the latest features. This guide walks you through updating and upgrading packages, as well as moving to newer releases, on several popular Linux distributions including Ubuntu, Debian, Fedora, CentOS, and Arch Linux.
Why Updating Linux Is Important
Regular Linux updates help protect your system from known vulnerabilities, fix bugs, and ensure compatibility with newer software and hardware. Unlike some operating systems, Linux updates are typically fast, transparent, and user-controlled, making it easy to stay current without disruption.
Updating Linux Packages for Ubuntu or Debian
To update Ubuntu, Linux Mint, or other Debian-based distributions, follow these steps:
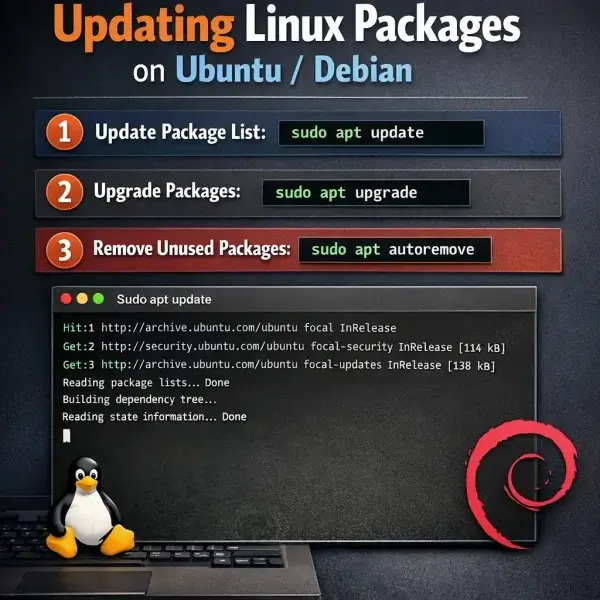
- Open a Terminal: Press Ctrl + Alt + T to open a terminal.
- Get the Latest Package List: Refresh the package database:
sudo apt update
This checks configured repositories for new versions.
- Upgrade Installed Packages: Install available updates:
sudo apt upgrade
When prompted, type Y to proceed.
- Clean Up Unused Packages and Cache:
sudo apt autoremove && sudo apt clean
This removes unused dependencies and clears cached package files.
Optional: Full Upgrade on Debian Based Systems
For larger system changes (such as kernel or dependency transitions), you can run:
sudo apt full-upgrade
This allows packages to be installed or removed if required to complete the upgrade.
Upgrading Ubuntu Distributions
To upgrade to a newer Ubuntu release:
sudo apt dist-upgrade
For moving between major Ubuntu releases (for example, 22.04 LTS to 24.04 LTS), it is recommended to use:
sudo do-release-upgrade
Ensure all packages are fully updated before running a release upgrade.
How to Update Fedora Linux
Fedora uses the dnf package manager, which combines updating, dependency handling, and cleanup.
- Open a Terminal: From the Applications menu or press Ctrl + Alt + T.
- Refresh metadata and upgrade packages:
sudo dnf upgrade --refresh
This command ensures you receive the latest available updates.
- Remove unused dependencies:
sudo dnf autoremove
This helps keep the system lean and efficient.
Upgrading Fedora
To upgrade Fedora to the latest release, use the dnf system-upgrade plugin:
sudo dnf install dnf-plugin-system-upgrade
sudo dnf system-upgrade download --releasever=version_number
sudo dnf system-upgrade reboot
Replace version_number with the target Fedora version. Fedora upgrades are generally smooth when performed shortly after a new release.
How to Update CentOS Linux
CentOS traditionally uses the yum package manager (or dnf on newer versions).
- Open a Terminal
- Update all installed packages:
sudo yum update
This checks repositories and installs available updates.
- Remove unnecessary packages:
sudo yum autoremove
This removes dependencies no longer required.
Upgrading CentOS
CentOS typically supports upgrades between minor releases (for example, 7.8 to 7.9). Major version upgrades often require a fresh install or migration to CentOS Stream, which follows a rolling-release model closer to Fedora.
How to Update Arch Linux
Arch Linux uses the pacman package manager and follows a rolling-release model.
- Open a Terminal:
- Sync repositories and upgrade packages:
sudo pacman -Syu
This single command keeps your entire system up to date.
- Remove orphaned packages:
sudo pacman -Rns $(pacman -Qdtq)
This removes dependencies no longer needed by any installed package.
Upgrading Arch Linux
Arch Linux does not have versioned upgrades. Running:
sudo pacman -Syu
on a regular basis ensures your system stays current with the latest software.
Best Practices for Updating Linux
- Update regularly to minimize large update jumps
- Read update prompts carefully, especially during major upgrades
- Back up important data before full system upgrades
- Reboot when kernels or core system libraries are updated
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
How often should I update my Linux system?
It’s recommended to update your Linux system at least once a week. Regular updates ensure you receive important security patches, bug fixes, and software improvements. Servers or security critical systems may require more frequent updates.
What is the difference between apt update and apt upgrade?
apt update refreshes the local package index by checking repositories for new versions. apt upgrade installs newer versions of packages that are already installed on your system.
Is it safe to use sudo apt autoremove?
Yes. sudo apt autoremove removes packages that were installed as dependencies but are no longer needed. Always review the list of packages before confirming to avoid removing something you still want.
How do I check my Linux distribution and version?
On Ubuntu or Debian-based systems, run:
lsb_release -a
On Fedora, CentOS, and most other distributions, use:
cat /etc/os-release
Do I need to reboot after updating Linux?
A reboot is usually only required after kernel updates or major system library upgrades. If a reboot is recommended, your system will often notify you.
Final Thoughts on How to Update Linux
Keeping Linux up to date is one of the simplest and most effective ways to maintain a secure and reliable system. Whether you use Ubuntu, Fedora, CentOS, or Arch Linux, understanding your package manager ensures smooth updates and long-term stability.
Remember to:
- Apply updates regularly
- Clean up unused packages to save disk space
- Follow official documentation for major upgrades
If you found this guide on updating Linux helpful, you may also want to read how to install Chrome on Linux.
