Updating Linux: Keeping your Linux system updated is essential for maintaining stability, security, and getting the latest features. This guide will walk you through updating and upgrading packages and moving to the latest release on several popular Linux distributions, including Ubuntu, Fedora, CentOS, and Arch Linux.
Updating Linux Packages for Ubuntu or Debian
To update Ubuntu, Linux Mint, or other Debian-based distributions, follow these steps:
- Open a Terminal: Press Ctrl + Alt + T to open a terminal.
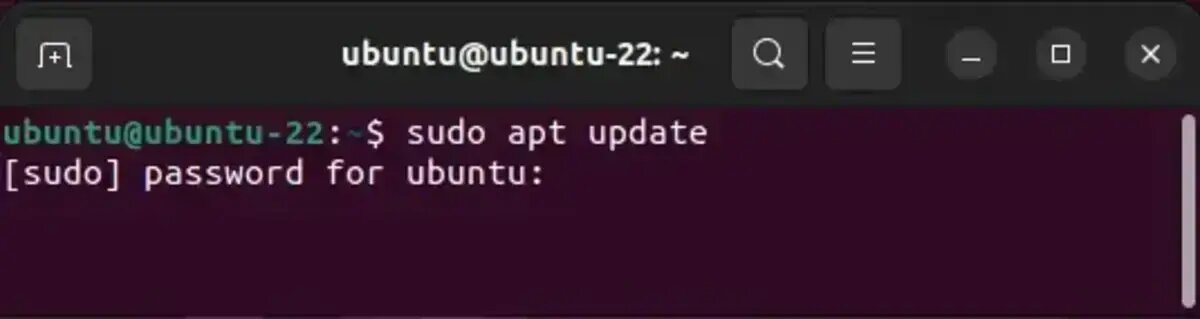
- Get the Latest Package List: Run the following command to refresh the package database:
sudo apt update
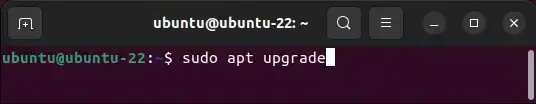
- Upgrade Installed Packages: Upgrade all installed packages by running:
sudo apt upgrade
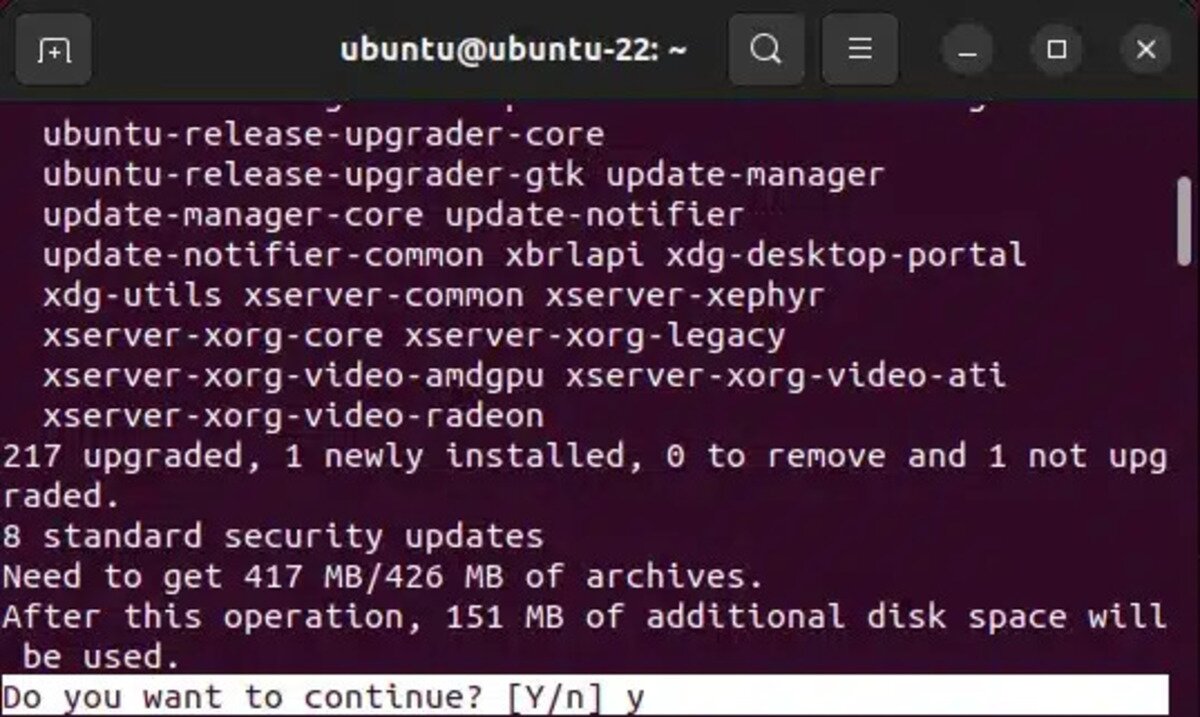
When prompted, type Y to proceed:
- Clean Up Unused Packages and Cache: Remove unneeded dependencies and clear cached packages using:
sudo apt autoremove && sudo apt clean
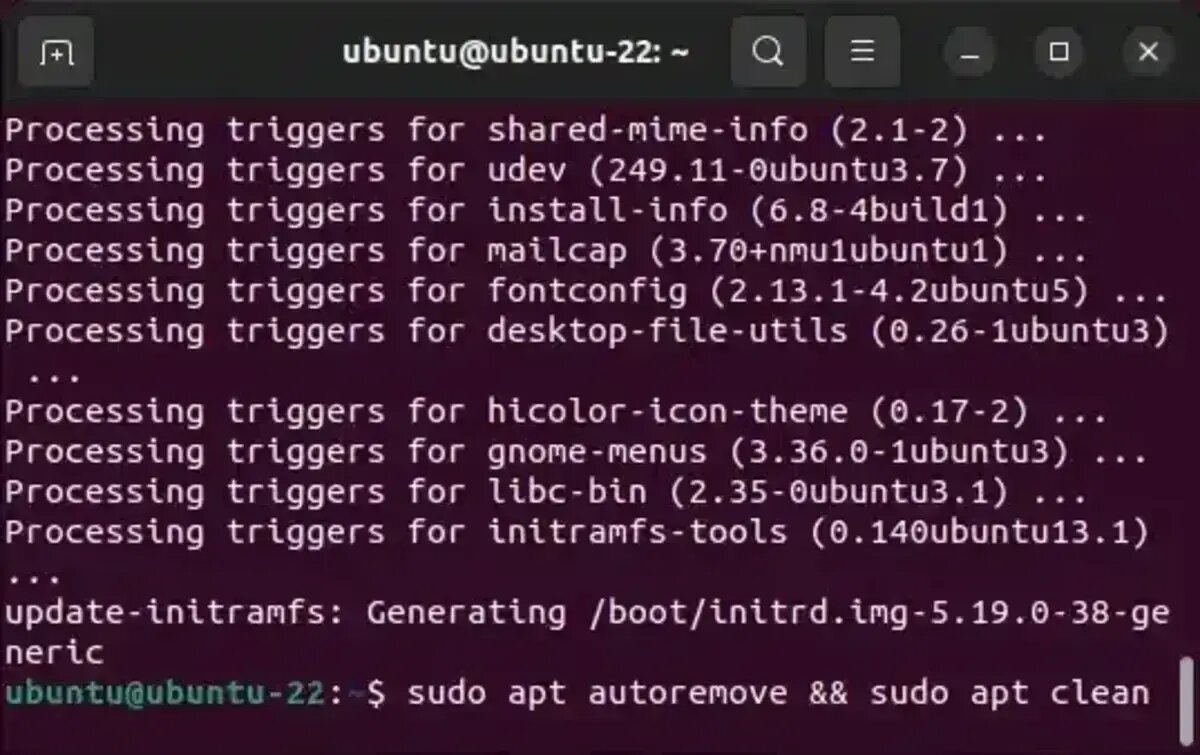
If prompted, confirm by typing Y:
Upgrading Ubuntu Distributions
To upgrade to the latest Ubuntu distribution, use:
sudo apt dist-upgrade
How to Update Fedora Linux
Fedora uses the dnf package manager. Follow these steps to update your system:
- Open a Terminal: Open from the Applications menu or by pressing Ctrl + Alt + T.
- Refresh and upgrade packages:
sudo dnf upgrade --refresh
This command updates the repository metadata and upgrades all installed packages.
- Remove unused packages:
sudo dnf autoremove
This command removes packages that were installed as dependencies but are no longer needed.
Upgrading Fedora
To upgrade Fedora to the latest release, use the dnf system-upgrade plugin:
sudo dnf install dnf-plugin-system-upgrade
sudo dnf system-upgrade download --releasever=version_number
sudo dnf system-upgrade reboot
Replace version_number with the latest Fedora release number.
How to Update CentOS Linux
CentOS uses the yum package manager, with commands similar to Fedora’s dnf.
- Open a Terminal:
- Update all packages:
sudo yum update
This command checks for available package updates and installs them.
- Remove unnecessary packages:
sudo yum autoremove
This will remove unneeded dependencies, freeing up disk space.
Upgrading CentOS
CentOS primarily supports upgrades between minor versions (e.g., 8.0 to 8.1). Major version upgrades (e.g., 7 to 8) may require a manual approach or dnf in CentOS Stream.
How to Update Arch Linux
Arch Linux uses the pacman package manager. Here’s how to keep it up to date:
- Open a Terminal: Open from the menu or press Ctrl + Alt + T.
- Sync package databases and upgrade:
sudo pacman -Syu
This command updates the package list and installs all package upgrades.
- Remove orphaned packages:
sudo pacman -Rns $(pacman -Qdtq)
This removes orphaned packages (dependencies no longer required by any installed package).
Upgrading Arch Linux
Arch Linux is a rolling-release distribution, so there are no separate distribution upgrades. Simply running the following command regularly will keep you on the latest version:
sudo pacman -Syu
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Here are some frequently asked questions regarding the essentials of updating Linux:
How often should I update my Linux system?
It’s recommended to update your Linux system at least once a week to ensure security patches and the latest software updates are applied.
What is the difference between apt update and apt upgrade?
apt update refreshes the package list, while apt upgrade installs newer versions of currently installed packages.
Is it safe to use sudo apt autoremove?
Yes, sudo apt autoremove removes unnecessary dependencies, but always double-check what will be removed before confirming.
How do I check my Linux version?
Use the following command for Ubuntu/Debian:
lsb_release -a
For Fedora and CentOS, use:
cat /etc/os-release
Final Thoughts on How to Update Linux
Keeping your Linux system updated is essential for security, stability, and access to the latest features. Whether you're using Ubuntu, Fedora, CentOS, or Arch Linux, following these steps will ensure your system stays optimized and protected.
Remember to:
- Update your system regularly to prevent security vulnerabilities.
- Use
autoremoveandcleancommands to free up disk space. - Check official Linux documentation for distribution-specific changes.
If you found this article on How to Update Linux helpful, you might also want to check out how to install Chrome on Linux.
