How to Get UUID of a USB Flash Drive on Windows, macOS, and Linux
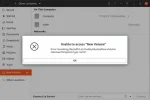
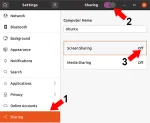
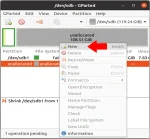
Get UUID: Need to quickly find the UUID of a USB flash drive for scripting, mounting, or system administration? Whether you're using Linux, macOS, or Windows, each system has its own method for identifying your device with a unique identifier like a UUID or volume serial. This comprehensive guide will help you locate the USB flash drive UUID on any major OS.